Measurements Used to Describe Crystal Structures
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms molecules or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern. The triclinic unit cell contains 12 molecules which form four hydrogen-bonded NHN trimers.

7 1 Crystal Structure Chemistry Libretexts
Now we know the typical distance between two.
. In the simple cubic crystal. The following points highlight the three main methods for determination of crystal structure of materials. Assumptions used to describe crystal structure i When describing crystalline from AA 1.
These can explain the experimentally observed. The crystal is illuminated. A map is constructed to describe the electron density of the molecules in the crystal.
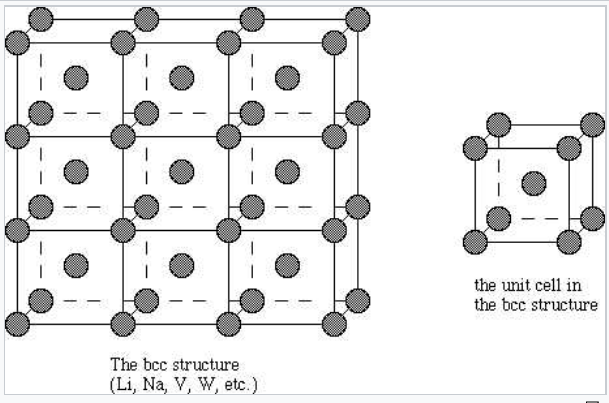
It turns out that the structures of binary ionic. The structure of a crystalline solid whether a metal or not is best described by considering its simplest repeating unit which is referred to as its unit cell. In this type of crystal structure one atom is situated at each corner of the unit cell as shown in the figure.
The atomic lattice is a three dimensional network of atoms that are arranged in a symmetrical pattern. Also the fractal dimen-sion measurement can provide valuable information about the crystal history and formation mechanisms. Rotating Crystal Method 3.
Crystal Structures of Some Common Binary Compounds We have now dealt with all of the possible cubic crystal structures for metals. Simple Cubic Crystal Structure SC. Not only that it is often used to reveal crystal size and morphology crystal.
A scheme by which crystal structures are. And as we can see this comes out to 0156 nanometers. The molecular and crystal structure of 3-nitropyrazole was determined by X-ray analysis.
See answer 1 Best Answer. As defined in the Measures Management System Blueprint structural quality measure also known as a structure measure assesses features of a healthcare organization or clinician relevant to. The goniometer is used to position the crystal at selected orientations.
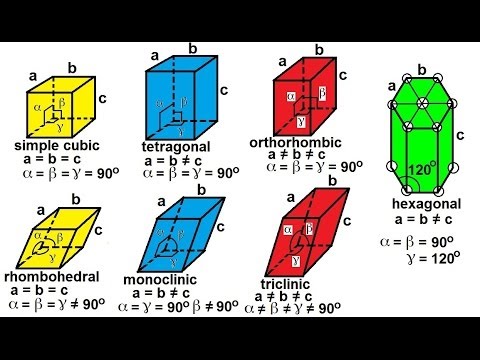
Atomic models of the molecules are also created. Careful measurement of mineral specimens allowed crystals to be classified in terms of six crystal families called anorthic monoclinic orthorhombic tetragonal hexagonal and iso-. The unit cell consists of lattice.
Atomic lattice or structure. In a single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurement a crystal is mounted on a goniometer. Laue Spot Method 2.
The combination of unit cell edge lengths a b c and inter-axial angles that defines the unit cell geometry alpha beta gamma crystal system. Powder diffraction XRD is a technique used to characterize the crystallographic structure crystallite size grain size and preferred orientation in polycrystalline or powdered solid samples. Transmission electron microscopy is a powerful tool to directly image crystal structures.
A b c abg90 Cube - is one of the easiest to recognize and many minerals display it with. The three crystallographic axes are all equal in length and intersect at right angles to each other. The shape of the lattice determines not only which crystal.
Also known as the isometric system. The key idea is that rugged and. Here we have outlined the basic atomic structure of the seven systems along with some common examples of each system.
So to find d we divide 00312 by 2 times the sine of 574 degrees.

Crystal Shapes Earth Sciences Museum University Of Waterloo
13 Crystal Structures Mineralogy

Chemistry Liquids And Solids 32 Of 59 Crystal Structure Seven Types Of Unit Cells Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment